Does A New Catalytic Converter Need A Break-In Period?
The catalytic converter is a relatively new addition to combustion engine vehicles. It’s a reasonably efficient component that filters out unwanted emissions harmful to the environment and humans. Most jurisdictions require an active converter to drive on the road, so replacements are common. But does your new convert need a break-in?
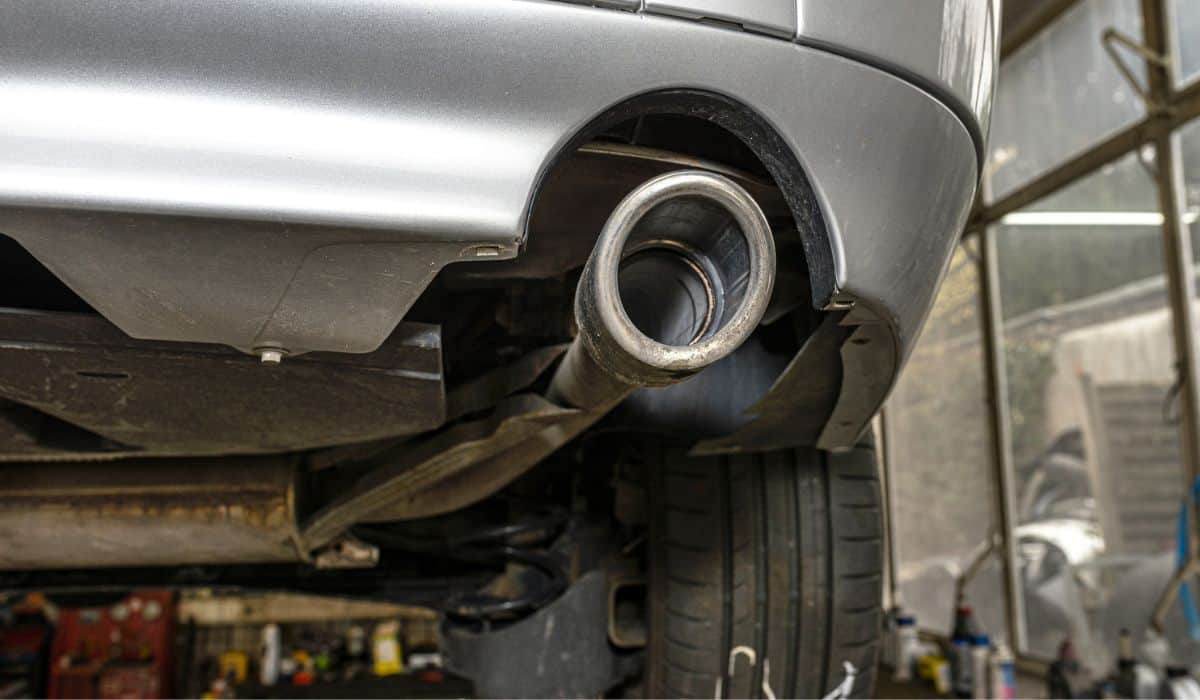

Yes, new catalytic converters require a “break-in” period. Without it, the interior components will become loose and damaged. The initial warm-up of a converter is simple and usually done by the mechanic. Be sure to ask your mechanic beforehand to avoid accidental damage to the vehicle.
You’ll need to know how to warm up your new parts if you’re about to replace your catalytic converter. Fortunately, we cover everything you need to know in the article below. Read on for more information.
Does a New Catalytic Converter Need a Break-in Period?
Yes, new catalytic converters require a “break-in” period. If the replacement converter isn’t warmed-up correctly, the substrate inside can become negatively affected and cause the component to break down.
This issue happens when a mechanic installs a replacement and returns the car to the customer too soon.
The owner drives off the lot and drives the car long distances or allows it to idle for extended lengths of time. In these situations, the interior matting that secures the substrate won’t expand correctly or hold its place.
Essentially, the converter matting is installed in an unexpanded condition. When it heats up for the first time, the matting expands and holds the interior components in place.
Interior components can become loose or damaged and rattle around if the warm-up isn’t done correctly.
How Do Catalytic Converters Work?
Combustion engines release harmful emissions, like CO2, NOx, and CxHx, that aren’t safe for humans or the environment.
As a result, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) started to enforce restrictions to reduce emissions in the 1980s—thus, the catalytic converter was born.
The catalytic converter is a foundational component of a vehicle’s exhaust system and filters exhaust gasses and harmful particles.
Catalytic converters look like large metal boxes on the underside of a vehicle and have two stages. Each stage has a honeycomb-like design constructed from a platinum alloy.
The first part is typically platinum-rhodium, while the second uses a platinum palladium design.
The harmful gasses flow through the honeycomb structure, and atom bonds break apart into nitrogen and oxygen—which is entirely harmless for the earth and humans.
Suggested Reading: Will A Clogged Catalytic Converter Cause Loss Of Power?
How to Assess When it’s Time for a New Catalytic Converter
Catalytic converters encounter issues all the time. They can develop clogs just like any other filter on a vehicle. Clogs and blockages typically occur on higher-mileage cars or older models.
You’ll notice some tale-tell signs of a faulty catalytic converter, including the following:
- Noticeable Performance Decrease: Performance drops are some of the first signs of a faulty catalytic converter. Your car might feel slow or sluggish. You might also notice a significant decrease in acceleration.
- Smoke Coming Out of the Exhaust: Once the catalytic converter fails, you’ll see dark-colored smoke expelling out of the exhaust pipe. The smell of the exhaust fumes will also change. You might notice a sulfur scent, which is common in failing converters.
When a catalytic converter fails, you have two options: purchase a replacement catalytic converter or remove the faulty one.
That being said, removing a catalytic converter makes driving a vehicle illegal on the street and is incredibly harmful to the environment.
Suggested Read: Will catalytic converter reduce exhaust smell?
How to Break In a New Catalytic Converter
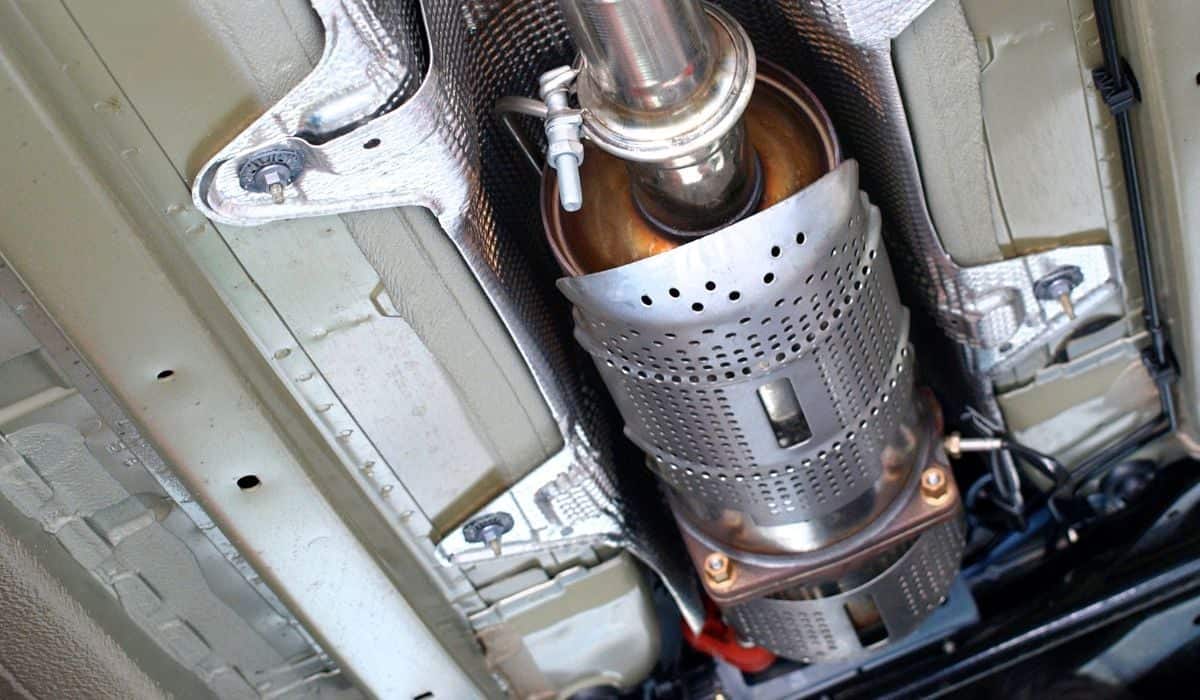
As mentioned earlier, breaking in a new catalytic converter is necessary for the installation process. The warm-up allows the interior components to be secure and prevents accidental damage. Your mechanic will typically warm up your new converter but double-check, just in case.
Here are the steps to break in a replacement catalytic convert:
- Start your vehicle. Do not apply any gas.
- Allow the vehicle to be idle and warm up.
- Let the engine reach its operating temperature or wait five minutes.
- Now, give enough gas to increase the engine to 2500 RPM.
- Hold power at 2500 RPM for 2 minutes and then release the gas pedal.
- Turn off the vehicle and allow it to cool down completely to finish.
Suggested Articles:
- New catalytic converter break-in period
- Can An Oil Change Affect Your Car’s Catalytic Converter?
- Can Seafoam Clean A Catalytic Converter?
- New catalytic converter smell
- Does catalytic converter affect fuel consumption
- What is the purpose of a catalytic converter?
- Rough Idle: Could A Clogged Catalytic Converter Be The Culprit?
